

CellReporterXpress Image Acquisition and Analysis Software
Easy-to-learn software optimized for automated microscopy using the ImageXpress Pico system
Microscopy imaging for cell counting through to complex image analysis
The CellReporterXpress Automated Image Acquisition and Analysis Software works with the ImageXpress® Pico system. It has a simple, easy-to-learn interface for performing quantitative analysis on images acquired from automated microscopy. The software enables distributed analysis of images for increased throughput and is ideal for scaling your digital microscopy imaging with slides or microplates. An icon-driven, linear workflow with a range of predefined protocols provides a streamlined user experience. With features such as Automated focus algorithms for a variety of applications including custom organ-on-a-chip plates, Digital Confocal 2D on-the-fly image deconvolution, and Live Preview advanced region of interest identification, you can save time while improving assay quality and significantly increasing resolution.

Analyze during acquisition
Reduce the time to run experiments with our integrated on-the-fly image analysis capability, allowing you to view numeric data during acquisition. In addition, our Digital Confocal option performs 2D image deconvolution in real-time allowing you to significantly increase resolution and assay quality.

Simplify image analysis
Predefined analysis protocols for label-free and fluorescence imaging provides you with the ability to quickly run common biological assays while still allowing you to create and save your own protocols. With optimized templates ranging from simple cell counting to complex neurite tracing, and including custom 2 and 3 lane Mimetas protocols, users no longer need to worry about adjusting complicated parameters or exporting to third-party software for robust analysis. With the addition of IN Carta® Image Analysis Software, you can leverage machine learning to get more information and increase accuracy in the analysis of your data to enable new discoveries with confidence.

Share and access data from anywhere
The software makes sharing, presenting, and collaborating with peers easier, allowing multiple users to utilize the software simultaneously through browser-based remote access.
https://view.ceros.com/molecular-devices/imagexpress-pico-digital-confocal/p/1
See what’s new with CellReporterXpress
Features

+25 preconfigured application protocols
User guided artificial intelligence routines optimize parameters automatically resulting in robust, easy-to-use analysis protocols.

Automated focusing routines for a variety cell-based imaging applications
Provides reliable focusing across all of your labware to ensure high-quality imaging for a wide variety of sample types.

Region selection for acquisition
Multiple unique positions within a well or slide can be selected to acquire and analyze only key areas of interest.
Label-free analysis
Automatically identifies objects in brightfield including small round cells, large cells, and beads.

Click-to-find feature
This feature auto calculates object parameters based on user-selected cells of interest, simplifying analysis setup for cell counting and for cellular responses.
Side-by-side cell magnification
Zoom or pan high-resolution images from whole well view down to cell level view. Simultaneously compare images from two wells.

Touch screen capability
Exceptional usability and precise control is built-in whether using a personal computer or a tablet.

Browser-based software
The ImageXpress Pico system can be controlled through a browser with data from any computer on the user’s network via Chrome™ or Safari®.
Intelligent image acquisition and analysis
CellReporterXpress software, along with the ImageXpress Pico system, does more than imaging—it offers unparalleled analysis capabilities that simplifies image analysis for cell-based assays.
Autofocus
Automated focus algorithms for a variety of applications
Two robust autofocus mechanisms: Detect Surface for hardware autofocus, and Find Best Plane for image-based autofocus. Provides reliable focusing across all of your labware to ensure high-quality imaging for a wide variety of sample types.
Digital Confocal
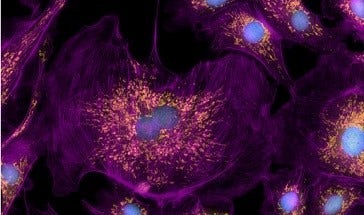
Increase resolution with on-the-fly deconvolution
Enhance contrast of images during acquisition with the Digital Confocal* 2D on-the-fly deconvolution option, allowing you to increase resolution and improve assay quality.
Live Preview
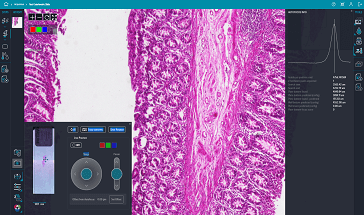
Identify regions of interest quickly and easily
Live Preview simplifies identification of regions of interest, letting you pan around the sample and interactively adjust focus with a virtual joystick, saving time and effort.
Environmental Control
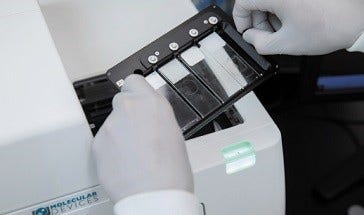
Monitor live cell assays with on-board environmental control
Multi-day, time-lapse, and live cell assays can be run using the on-board environmental system with options for humidity, CO2, and O2 control. Optimized to prevent Z-drift, the software also provides real-time monitoring of environmental state, ensuring optimal assay conditions.
Multi-wavelength Cell Scoring
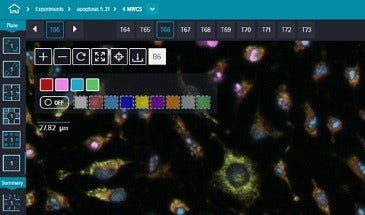
Features multi-wavelength cell scoring with up to four fluorescent stains
The preconfigured protocol is ideal for counting and logging measurements of cells in multiple wavelength experiments. Using a fluorescent marker for the nucleus and additional markers for the cytoplasm, each wavelength is analyzed and cells are assigned multiparametric phenotypic profiles.
Z-stack Acquisition
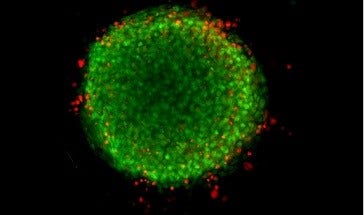
Capture deeper insights with Z-stack acquisition
Generate sharper images for more accurate segmentation using Z -stack acquisition. Acquire a series of images at different focal points to capture more detail than with a single slice. Users can include all slices or select which slices to include in the final projection.
Save time and reduce errors with preconfigured analysis protocols
Over 25 preconfigured analysis protocols ranging from simple cell counting to sophisticated neurite tracing analysis. With features like the click-to-find tool, analysis parameters can be optimized by simply clicking on a few cells that match specific criteria.
Click on the icons below for additional information on each of the CellReporterXpress capabilities
CellReporterXpress is part of the ImageXpress Pico Automated Cell Imaging System. To learn more, please visit the ImageXpress Pico product page.
Digital microscopy with automated brightfield, fluorescence, and Digital Confocal imaging
- Ideal for cell counting, transfection efficiency, and cell health assays
- Hardware autofocus uses an LED beam to find reflective surfaces and is designed for speed
- Monitor live cell assays with on-board environmental control
- Browser-based, tablet and touchscreen compatible software
- Tailored laboratory automation solutions with robotics, incubators, and software