
Cell Line Development Workflow
Workflow for generating recombinant proteins from cell lines such as CHO, Hybridoma or HEK 293.
Cell line development for recombinant proteins
In order to generate high yields of recombinant protein products, cell lines such as CHO, Hybridoma or HEK 293 are typical platforms of choice. The process of developing stable cell lines starts with transfecting host cells (CHO or HEK 293) with recombinant plasmids or cell fusion for hybridomas. After transfection or cell fusion, large numbers of clones are screened and selected on the basis of expression of protein of interest (therapeutic biologics). Once candidate clones are identified, each “hit” is confirmed, validated, and characterized using DNA sequencing and a variety of downstream analytical assays. Upon completion, the lead clones are expanded and scaled up where bioprocesses occur.
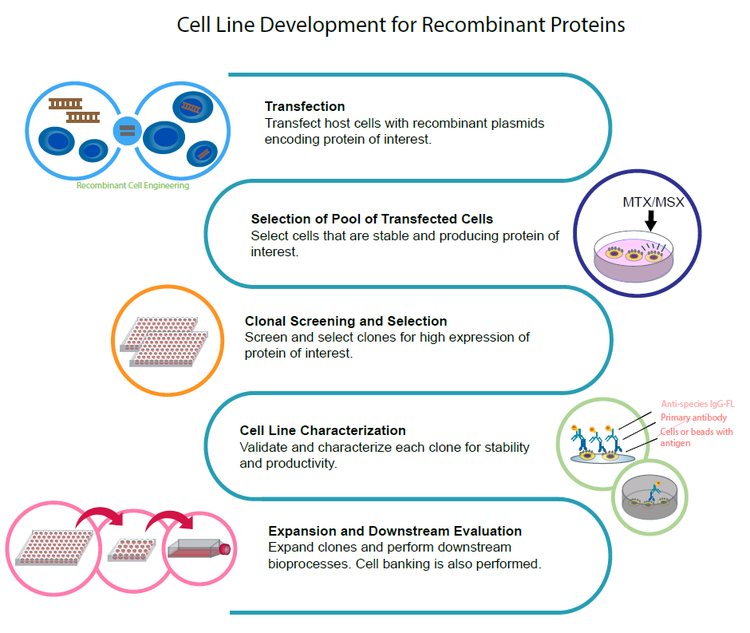
Stages of a typical cell line development process
Workflow for generating recombinant proteins
- Transfection - Transfect host cells with recombinant plasmids encoding a protein of interest.
- Selection of Pool of Transfected Cells - Select cells that are stable and producing protein of interest.
- Clonal Screening and Selection - Screen and select clones for high expression of protein of interest.
- Cell Line Characterization - Validate and characterize each clone for stability and productivity.
- Expansion and Downstream Evaluation - Expand clones and perform downstream bioprocesses. Cell banking is also performed.