What is live cell imaging?
Benefits of live cell research
Live cell imaging is a fundamental research tool in cell biology labs and in a wide variety of industries, and it has led to the discovery of drug targets and candidates as well as the molecular mechanisms involved in diseases. Critical for these researchers, is the ability to develop assays that can best mimic the in vivo nature of cells. Benefits of imaging live cells include:
- Monitoring live cells over time provides more than a snapshot of what is occurring in the cells while allowing for the visualization of transient events that may be missed in end-point assays and revealing optimal time-points for end-point assays.
- Tight regulation of environmental conditions ensures that the cellular structures and processes being studied are in their native physiological state
- Imaging live cells in their natural state minimizes artifacts that can arise from other imaging techniques, such as cell fixation and immunostaining.
- The localization and transport of cellular biomolecules along with the progression of multiple pathways can be investigated simultaneously in real-time.
- Acquiring images laterally, axially, and temporally enables the generation of 4D images and data
- Live cell imaging of molecular dynamics generates qualitative and quantitative data that can’t be gained from other biochemical methods.
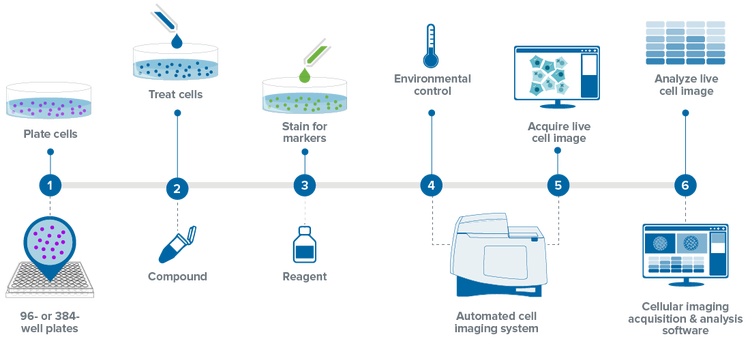
Cellular imaging and analysis workflow
Protocols for culturing, plating, and maintaining live cells will vary between different cell models however, the steps below outlines a generalized workflow for live cell assays.
- Plate cells into labware of choice (chamber slides, dishes, microplates)
- Treat cells – Perform cell treatments with desired compounds, RNAi, etc. if part of the assay workflow.
- Stain for markers – If required, label cells with the desired fluorophores (fluorescent dyes, fluorescent protein – peptide fusions, etc.
- Environmental controls – If the acquisition will take a long time or if the assay is a live cell time-lapse experiment (continuous or discontinuous), then enable full environmental control including gas, temperature, and humidity.
- Acquire cell image – Place the plate into the automated imaging system and start acquiring your live cell images
- Analyze cell image – Use cellular imaging analysis software to run quantitative analysis of live cell images
Live cell imaging system
Sophisticated live cell imaging systems provide the ability to regulate environmental conditions to maintain the health and viability of cells while monitoring molecular and cellular dynamics from the single cell to organismal level. From the study of fast-kinetic events to running long-term, time-lapse assays, automated live cell imaging provides the direct observation of dynamic biological processes and the ability to generate a wealth of cellular information
- Label-free, brightfield imaging to multi-color fluorescence imaging capabilities provide the flexibility necessary for the multitude of live cell imaging applications
- High-acquisition speeds allow for the examination of fast-kinetic events, such as calcium oscillation in cardiomyocytes.
- Robust focusing capabilities of automated live cell imaging instruments ensure the maintenance of optimum focus through the entirety of the acquisition, which is crucial for generating accurate live cell imaging data.
Applications and assays
Advancements in automated microscopes with integrated environmental control chambers as well as in fluorescent protein and synthetic fluorophore technology have expanded the capabilities of researchers investigating biological processes in living cells.
Our systems for high-content imaging and analysis provide flexible scalability making it easy to evolve your system alongside your research. They feature options and modules to address your specific research needs including objectives, filters, imaging modes, and environmental control. Here we have a collection of applications and assays that utilize these key features for your live cell imaging research:
Latest Resources
Live Cell Imaging and Analysis Workflow
The described live cell imaging workflow is a generalized example of a continuous long-term time-lapse live cell assay. This workflow breaks down the steps from cell plating to image analysis and highlights the materials and instrumentation necessary to run a live cell assay including an automated high-content imaging system and cellular imaging and analysis software.
Live Cell Imaging & Analysis Workflow

PLATE CELLS
Plate adherent or suspension cells into the labware of choice including culture dishes, chamber slides, and microplates. Incubate the cells at normal culture conditions (i.e. 37°C, 5% CO2). For adherent cells, incubating the plated cells overnight will allow ample time for cell attachment and growth.

96- or 384- Well Plates
Most cell cultures for high-content, high-throughput screening are run using 96- or 384-well microplates.

TREAT WITH COMPOUNDS
If necessary for the protocol, treat the cells with compounds of interest.
Compounds can be added to cells for minutes up to several days depending on the mechanism of action of the compounds and the biological re-sponse being investigated. For example, apoptosis or receptor internalization assays generally require shorter incubation periods while multiparametric cytotoxicity assays require longer periods. Longer compound treatments may require the replacement of compounds during incubation.

STAIN FOR MARKERS
Live cells can be stained with a variety of fluorophores or transfected/transduced with constructs containing fluorescent protein – peptide fusions. Manufacturer instructions should be followed when staining. Stain-ing isn’t necessary for all live cell applications and label free imaging and analysis allows for the tracking and monitoring of cells in brightfield only.

Assay Kits
Easy-to-use, robust assay kits for life science research, drug discovery and development, and bioassays. Our assay kits are optimized for use on our instruments. Screen more compounds earlier in drug discovery and enable characterization of a full concentra-tion-response profile of test compounds.

ImageXpress High-content Imaging Portfolio
Our systems for high-content imaging and analysis provide flexible scalability making it easy to evolve your system alongside your research. They feature options and modules to address your specific research including objectives, filters, imaging modes, and envi-ronmental conditions.

CONFIGURE ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL SETTINGS
After the addition of stains and compounds, place the plate into the appropriate imaging instrument integrated with environmental control capabilities such asl gases (CO2, O2), temperature, and humidity.
For long-term time-lapse assays it is essential to maintain a natural physiological environment to ensure the health of living cells and to prevent focus drift throughout the time-lapse acquisition.

ACQUIRE LIVE CELL IMAGE
For continuous time-lapse acquisitions, configure the total length of time for the time series and the imaging intervals, i.e. image every hour for 24 hours.
Discontinuous time-lapse acquisitions can be per-formed, where the plate is taken to and from the incubator and imaged at different time points.
https://vids.moleculardevices.com/watch/Z3iBwKY6jzq5BkFsqDfjBi
Automated Cell Imaging System
The ImageXpress® Pico Automated Cell Imaging System is more than a digital microscope, combining high-resolution imaging with powerful analysis. Whether running fluorescence imaging or brightfield assays, the automated imager features comprehensive preconfigured protocols for cell-based assays to shorten the learning curve, so you can start running experiments quickly.
https://vids.moleculardevices.com/watch/7gQUWFhYh9tQ5umAw39jzK
Cellular Imaging Acquisition and Analysis Software
The CellReporterXpress Automated Image Acquisition and Analysis Software works with the ImageXpress® Pico systems. It has a clean, easy-to-learn interface for performing quantitative analysis on images acquired from automated microscopy. The software enables distributed analysis of images for increased throughput and is ideal for scaling microscopy imaging with slides or microplates.

ANALYZE LIVE CELL IMAGE
Analyze the images with cellular imaging analysis software to generate multiparametric readouts for the biological responses that are being studied. Kinetic data can be generated and reviewed for time-lapse acquisitions.