
Cancer Research Solutions
Understand cellular pathways and interactions in cancer research with 3D imaging
Cancer therapeutic screening with 3D imaging of spheroids, organoids, and organ-on-a-chip systems
Cancer involves changes which enable cells to grow and divide without respect to normal limits, to invade and destroy adjacent tissues, and ultimately to metastasize to distant sites in the body. Cancer researchers need tools that enable them to more easily study the complex and often poorly understood interactions between cancerous cells and their environment, and to identify points of therapeutic intervention.
Learn about our automated cell culture system, high-content imaging systems, and analysis software solutions that facilitate cancer research using biologically relevant 3D cellular models like spheroids, organoids, and organ-on-a-chip systems to simulate the in vivo environment of a tumor or organ.

Patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids. Blue: nuclei, green: actin, red: mitochondria.
Advantages of 3D imaging technology for cancer spheroids
Cancer spheroids mimic tumor behavior far more effectively than standard 2D cell cultures. Such 3D spheroid models are being successfully used in screening environments for identifying potential cancer therapeutics. These culture systems can be used in multiparametric analysis to quantify different biological outputs, accelerating cancer drug development.
Key benefits include:
- The development of 3D high-content imaging signifies a major step in facilitating more relevant and accurate testing
- 3D culture systems can rapidly produce uniform human cancer cell spheroids that can be used in high-throughput format to accelerate cancer drug development
- Research with confocal 3D image analysis of cancer cells has enabled multiparametric characterization of many biological outputs
Workflow for analyzing 3D cancer spheroids in high-throughput screening environment
Spheroids can be grown in 96- or 384-well plates, treated with compounds, and stained with dyes that reveal the cellular processes and pathways at work. In some cases, spheroids can be imaged without washing; they may also be fixed if desired.
Simplify your oncology workflow with a broad range of imaging, cellular screening, and microplate reader systems.
The workflow illustrates a simplified process for analyzing spheroids and highlights systems to help you streamline research and increase your throughput.
Culture spheroids – Cancer cells can be cultured directly in an ultra-low attachment (ULA), round bottom plate, or other labware to develop the typical morphology of a spheroid. Other labware allows one to grow multiple spheroids in a single well.
Treat with compounds – After spheroid formation, compounds at the desired concentrations are added into the wells, and then incubated for one to several days, depending on the mechanism being studied.
Stain for markers – After compound treatment is complete, stains are added directly to the media. Stains that require no washing can be used to avoid disturbing spheroids, but spheroids can be carefully washed, even using automation, if necessary.
Acquire spheroid images – Images within the body of the spheroid can be captured individually or as a z-stack (multiple images taken at differing depths) using specialized imaging equipment.
Analyze cancer cells – Use cellular imaging analysis software to run quantitative analysis of the cell images to monitor the expression of different markers and to quantify biological readouts.
High-throughput confocal imaging of spheroids for screening cancer therapeutics
In recent years, there has been significant progress in development of in vitro aggregates of tumor cells for use as models for in vivo tissue environments. When seeded into a well of a low-attachment round bottom microplate, these aggregates will form a discrete spheroid. Spheroids are believed to mimic tumor behavior more effectively than regular two dimensional (2D) cell cultures because, much like tumors, they contain both surface-exposed and deeply buried cells, proliferating and non-proliferating cells, and a hypoxic center with a well-oxygenated outer layer of cells. Such 3D spheroid models are being successfully used in screening environments for identifying potential cancer therapeutics.
While there are several challenges to developing robust spheroid assays, using automated high-throughput, high-content imaging is a significant step in facilitating more relevant testing of chemotherapeutic drug candidates
- Capture an entire spheroid in one field-of-view at 20X magnification
- Screen biologically relevant 3D spheroids in 96- or 384-well format
- Use confocal imaging to accurately detect cellular responses
- Conserve storage space by saving only 2D reconstructions of the z plane images
Figure 1. Rapidly screen 3D spheroids in microplates
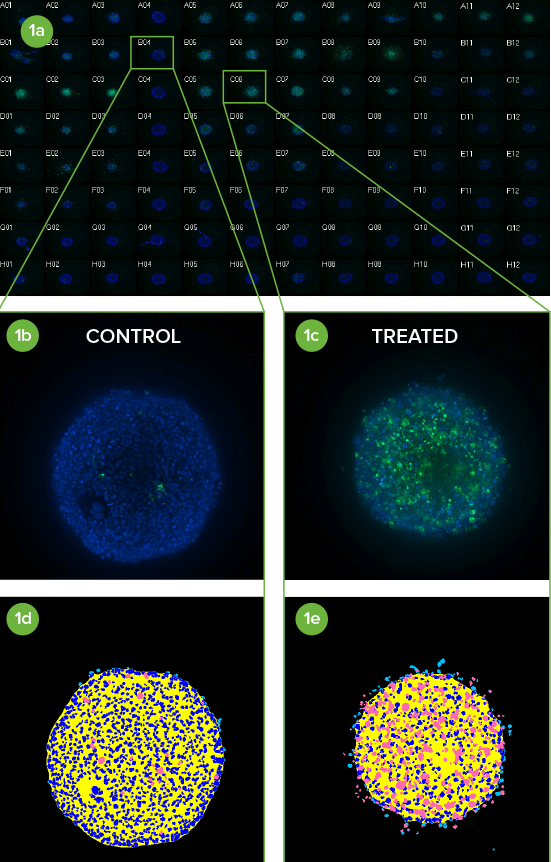
(1a) Montage of image thumbnails of HCT116 spheroids in a 96-well plate treated with compounds and imaged with a 10X Plan Fluor objective. Hoechst stained nuclei (blue) are overlaid with CellEvent Caspase 3/7 apoptosis marker (green).
(1b) Untreated controls are in column 4 and (1c) a Caspase 3/7 response is evident in columns 5–7 where Paclitaxel was serially diluted 1:3 from 1 µM in Row A (replicates of 3 across).
(1d, 1e) Eleven z planes were combined into a 2D Maximum Projection image and analyzed with a simple custom module. Raw images showing low and high degree of apoptosis with their corresponding segmentation masks are shown (royal blue = nuclei, pink = apoptotic cells).
Applications and assays
Molecular Devices, an industry leader in solutions for complex biology, provides a wide range of tools to support life science research, drug discovery, and high-throughput screening. Our AI-driven automated cell culture and high-content imaging systems can drive the success of your bioanalytical cancer research efforts. We also provide several configurations of our multi-mode microplate readers as well as a line of easy-to-use microarray scanners.
Learn more about how our technology can help your research in cancer therapeutics.