
What is the voltage-clamp method?
Voltage-clamp allows the investigator to control the transmembrane voltage and subsequently measure current flow through an ion channel after activation. An ion channel can be activated by either a change in transmembrane voltage or a selective ligand, acting as a switching mechanism.
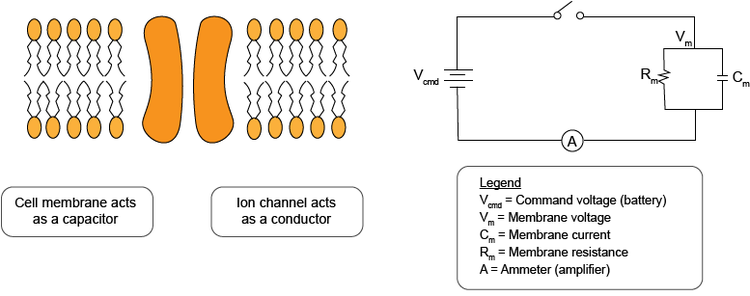
Figure. The cellular membrane as a simplified circuit.
In an experiment using the voltage-clamp method, one controls the membrane voltage in a cell and measures the transmembrane current required to maintain that voltage. The ideal voltage-clamp circuit simply consists of a battery, a switch, a wire, the cell and an ammeter. In an experiment, one controls the membrane voltage and measures the transmembrane current required to maintain that voltage.
- When the switch closes, the membrane potential steps instantly to the battery voltage. For simplicity, it is assumed that V m =0 before the step.
- There is an impulse of current injecting a charge Q=C m Vcmd ; the steady-state current is Vcmd /Rm.
- In this experiment, the voltage is the independent variable. Its value is controlled and equal to the battery value.
- The current is the dependent variable; its value is measured by an ammeter. For this reason, the voltage-clamp circuit is sometimes called a "current follower".
For more information, please download our Axon Guide.
Other links: