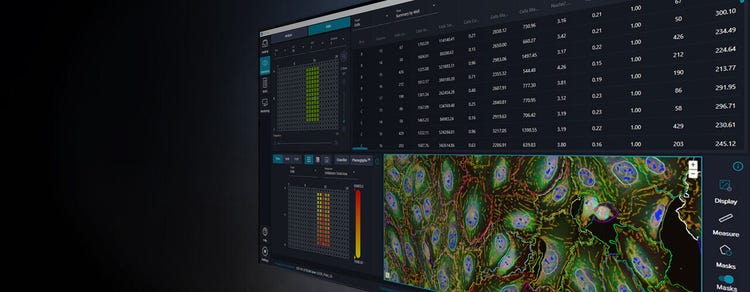
IN Carta Image Analysis Software
Provides robust, quantitative results from complex biological images and datasets
Go from assay to insights quickly and reliably with ImageXpress imaging systems and IN Carta software
IN Carta® Image Analysis Software solves complex image analysis problems utilizing advanced Artificial Intelligence (AI) transforming images into results, which can be interpreted with ease. User-friendly workflows help you get answers faster from 2D, 3D, and 4D experiments. With the integration of our Custom Module Editor application, you can define highly customized image analysis protocols allowing you to obtain robust results—even for complex assays—then quickly visualize, review, and interact with the analysis results. Let IN Carta software do the heavy lifting so you can focus on your research.

Powerful
Guided workflows and scalable batch processing increase productivity and reduce time to answer. Experiments can be set up quickly and analysis of multiple wells is run in parallel.

Insightful
Machine learning helps you leverage more information and increase accuracy in the analysis of high-content screening data to enable new discoveries with confidence.

Intuitive
Modern user experience and cutting-edge technology minimizes the software learning curve and removes barriers to productivity.

IN Carta Image Analysis Software
Features

Deep learning
Improve specificity of your image analysis workflows by utilizing the SINAP module. SINAP relies on deep learning-based image analysis, resulting in robust segmentation for virtually any biological structure.

Start with a worklist
Browse to a parent directory and populate your worklist with image datasets of interest or simply use search to find them.
AI-powered data analytics
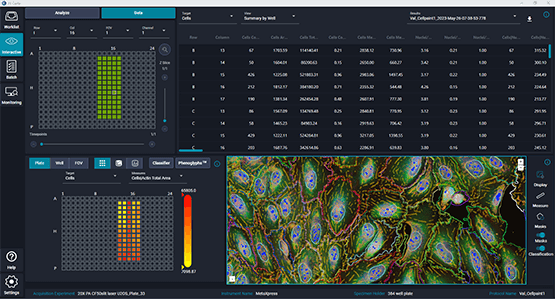
Leverage the power of machine learning without being a data scientist. Identify and quantify phenotypic changes in a user-friendly workflow. Explore your data and reveal insights from complex datasets. Find novel and unexpected phenotypes with a few mouse clicks.

Customization
Browse and review images from experiments, create image analysis protocols of different complexity and add on-demand data classification. Visualize analysis results using 360 ̊ data linking among images, data table and charts.

3D analysis
The Custom Module Editor’s 3D application provides unprecedented flexibility in segmenting complex biological structures. Image datasets can be acquired in 3D or 4D (timelapse 3D) and tailored image analysis routines can be developed within a guided workflow.

Batch analysis and monitoring
Analyze multiple experiments in batch analysis mode with one or more analysis protocols. Monitor the status of all submitted tasks and oversee their progression in real time.
Flexi-Protocol
Flexi-Protocol application allows to create custom analysis protocols of various complexity by adding as many analysis steps is needed. Each analysis step can contain image pre-processing and object mask post-processing operation to better adapt to a specific assay. Redesigned analysis and image viewer panes can be expanded or collapsed depending on where focus is needed.
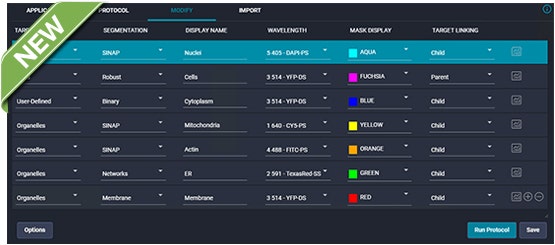
- Simple or complex – create any analysis protocol you require for the assay of interest. Segment and extract measurements from any number of channels
- Tailored – define target hierarchy in the protocol via target linking. Use Custom Measure option to calculate additional measurements for any of the biological targets
- Compelling – leverage deep learning segmentation option at any of the analysis steps. Target masks can be combined using logical operations
- Easy to use – intuitive user interface with dynamic panes enables focused protocol development
- Help is just a click away – easily access contextual help with an interactive, searchable user guide
IN Carta SINAP
SINAP is a module that uses deep learning algorithms to improve accuracy and reliability of high-content screening assays at the first step in the analysis pipeline—segmentation. It provides better object detection than traditional image analysis methods. Deep learning models can be easily tailored within a user-friendly tool, so that any novel biological objects can be segmented efficiently. Quantitative information extracted from segmented objects is more accurate, so errors are not propagated down the analysis pipeline.
With SINAP, Segmentation Is Not A Problem!
- Accurate – deep learning can maintain accuracy across difficult to segment samples including confluent cells, low signal-to-noise samples and transmitted light images
- Reliable – SINAP models can account for high phenotypic variability
- Flexible – a single workflow can deal with a variety of applications and imaging modalities
- Accessible – trained model learns to segment from scientist’s drawing on the image rather than asking a deep-learning guru to create a new model and optimize multiple parameters
Customized SINAP deep-learning models segment specific regions (whole body, head, eyes, brain) of a zebrafish embryo in transmitted light image. Courtesy of Guo Lab, UCSF
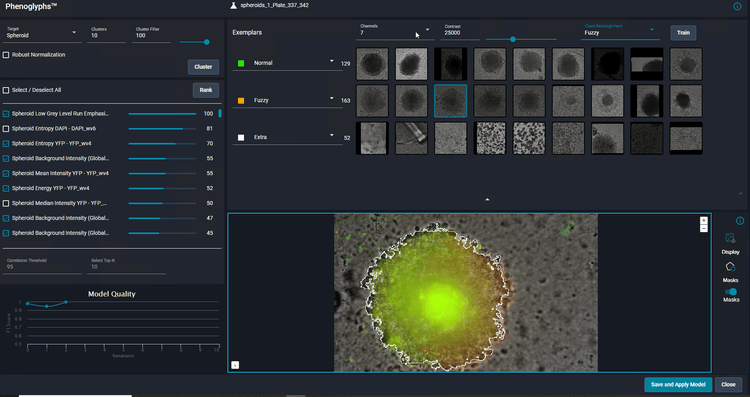
IN Carta Phenoglyphs
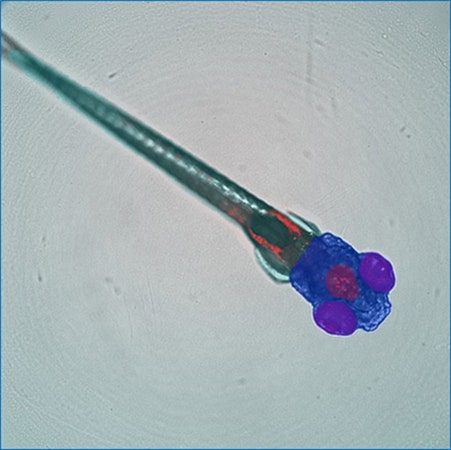
IN Carta® Phenoglyphs™ Software Module uses a unique combination of unsupervised and supervised machine learning to quantify phenotypical changes. Using many hundreds of cellular features that can be analyzed simultaneously, a comprehensive phenotypic profile is created and can be applied throughout an entire screening workflow. This multivariate approach to classification provides accurate characterization of object populations allowing users to resolve subtle phenotypic changes induced by drug treatment or genetic modification. It can be utilized across many biological targets including organoids, cells, spheroids, and more.
Classification of spheroids formed from HCT116 cells. Spheroids were segmented based on brightfield images using SINAP. Sample was additionally counter-stained with with Hoechst 33342, Calcein AM and MitoTracker Red to visualize nuclei, live cells and mitochondria respectively.
- Comprehensive – a data driven approach that starts with an unsupervised clustering to find patterns in the data and highlight subpopulations without prior knowledge of what phenotypes may exist.
- Robust – dedicated machine learning algorithm identifies the optimal set of descriptive features to avoid overfitting of the resulting classification model.
- Optimized workflow – classification is achieved by simply confirming or correcting the algorithm’s predictions until it learns the right behavior.
IN Carta Custom Module Editor 2D and 3D
- Create simple step-by-step custom analysis
- Tailor object segmentation and classification
- Find objects localized within defined biological compartments
- Report only measurements required for an assay of interest
- Analyze live imaging data
- True 3D segmentation (3D application only)
- Robust reconstruction of 2D segmentation into volume for 3D assays (3D application only)

Example segmentation of HCT116 cells forming a spheroid segmented in Custom Module Editor 3D and visualized in 3D viewer
ImageXpress HCS.ai system
A fast, intuitive and versatile system delivering deeper insights for every lab
- Ideal for a vast range of imaging assays - from basic cell analysis to highly complex multiplexed and 3D assays
- Configurable to match your requirements, with a simple upgrade path to meet evolving research needs
- Options for seven-channel high-intensity lasers, spinning confocal disk technology for deeper tissue penetration, environmental control, water immersion objectives and much more!
- New MetaXpress Acquire software offers an intuitive solution for users of all experience levels
Latest Resources
Customer Breakthrough
Applications of IN Carta Image Analysis Software
Resources of IN Carta Image Analysis Software
Explore our high-content imaging portfolio
High-content imaging and analysis solutions, ranging from automated digital microscopy to high-throughput confocal imaging systems with water immersion objectives and proprietary spinning disk technology.
